07 查询:DSL查询之复合查询详解
复合查询引入
在(前文-多条件查询-bool)中,我们使用bool查询来组合多个查询条件。
比如之前介绍的语句
1 | GET /bank/_search |
这种查询就是本文要介绍的复合查询,并且bool查询只是复合查询一种。
bool query(布尔查询)
通过布尔逻辑将较小的查询组合成较大的查询。
概念
Bool查询语法有以下特点
- 子查询可以任意顺序出现
- 可以嵌套多个查询,包括bool查询
- 如果bool查询中没有must条件,should中必须至少满足一条才会返回结果。
bool查询包含四种操作符,分别是must,should,must_not,filter。他们均是一种数组,数组里面是对应的判断条件。
must: 必须匹配。贡献算分must_not:过滤子句,必须不能匹配,但不贡献算分should: 选择性匹配,至少满足一条。贡献算分filter: 过滤子句,必须匹配,但不贡献算分
一些例子
看下官方举例
- 例子1
1 | POST _search |
在filter元素下指定的查询对评分没有影响 , 评分返回为0。分数仅受已指定查询的影响。
- 例子2
1 | GET _search |
这个例子查询查询为所有文档分配0分,因为没有指定评分查询。
- 例子3
1 | GET _search |
此bool查询具有match_all查询,该查询为所有文档指定1.0分。
- 例子4
1 | GET /_search |
每个query条件都可以有一个_name属性,用来追踪搜索出的数据到底match了哪个条件。
boosting query(提高查询)
不同于bool查询,bool查询中只要一个子查询条件不匹配那么搜索的数据就不会出现。而boosting query则是降低显示的权重/优先级(即score)。
概念
比如搜索逻辑是 name = ‘apple’ and type =’fruit’,对于只满足部分条件的数据,不是不显示,而是降低显示的优先级(即score)
例子
首先创建数据
1 | POST /test-dsl-boosting/_bulk |
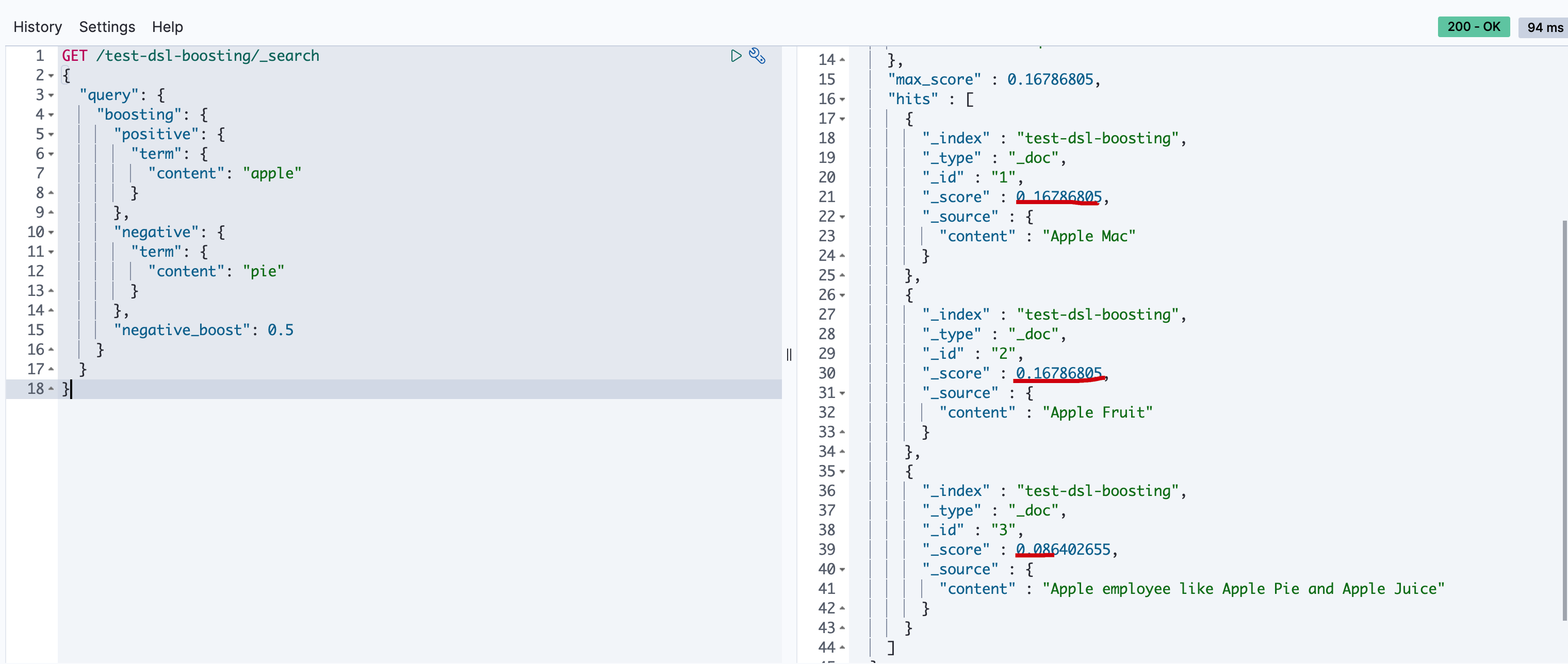
对匹配pie的做降级显示处理
1 | GET /test-dsl-boosting/_search |
执行结果如下
constant_score(固定分数查询)
查询某个条件时,固定的返回指定的score;显然当不需要计算score时,只需要filter条件即可,因为filter context忽略score。
例子
首先创建数据
1 | POST /test-dsl-constant/_bulk |
查询apple
1 | GET /test-dsl-constant/_search |
执行结果如下

dis_max(最佳匹配查询)
分离最大化查询(Disjunction Max Query)指的是: 将任何与任一查询匹配的文档作为结果返回,但只将最佳匹配的评分作为查询的评分结果返回 。
例子
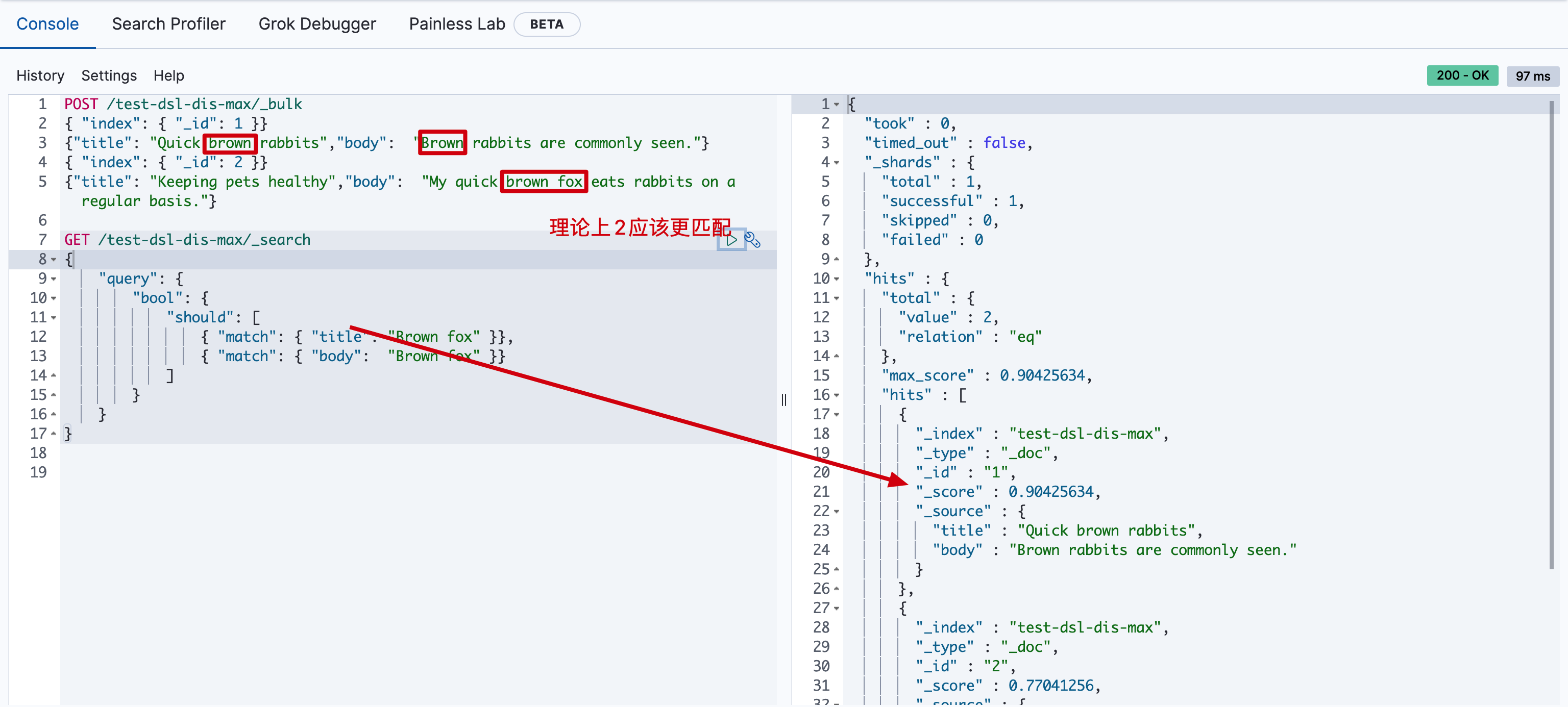
假设有个网站允许用户搜索博客的内容,以下面两篇博客内容文档为例:
1 | POST /test-dsl-dis-max/_bulk |
用户输入词组 “Brown fox” 然后点击搜索按钮。事先,我们并不知道用户的搜索项是会在 title 还是在 body 字段中被找到,但是,用户很有可能是想搜索相关的词组。用肉眼判断,文档 2 的匹配度更高,因为它同时包括要查找的两个词:
现在运行以下 bool 查询:
1 | GET /test-dsl-dis-max/_search |
为了理解导致这样的原因,需要看下如何计算评分的
- should 条件的计算分数
1 | GET /test-dsl-dis-max/_search |
要计算上述分数,首先要计算match的分数
- 第一个match 中
brown的分数
doc 1 分数 = 0.6931471
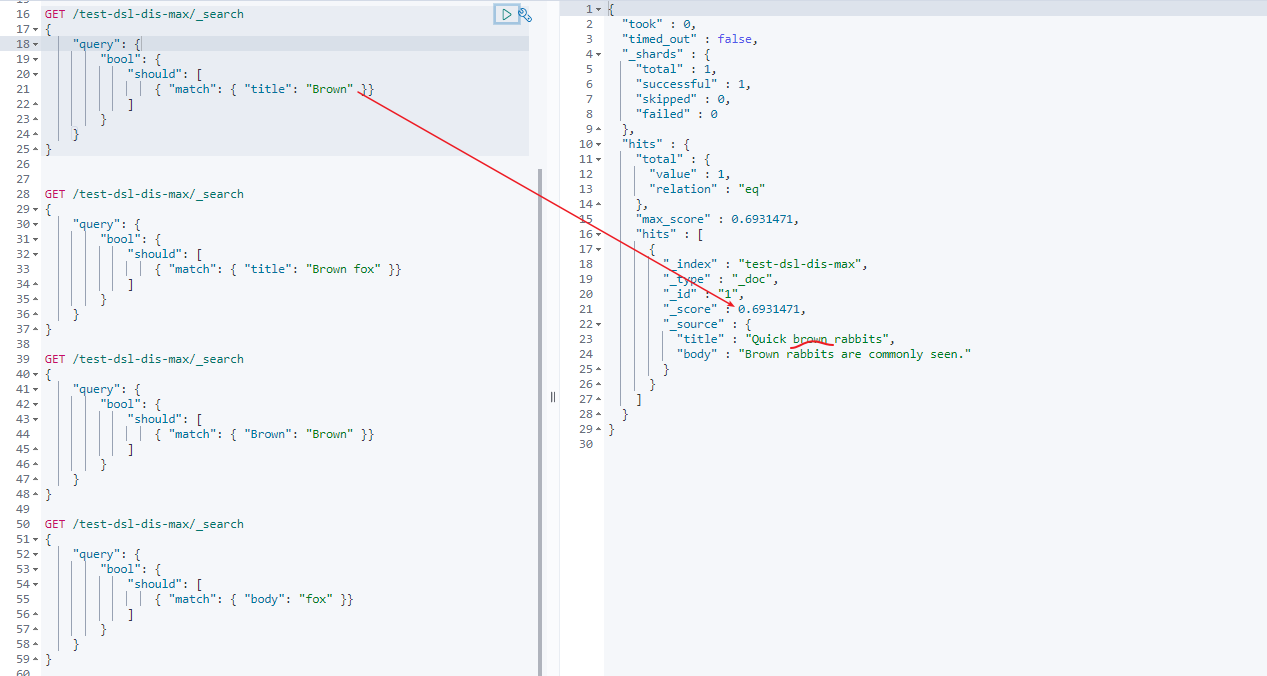
- title中没有fox,所以第一个match 中
brown fox 的分数 = brown分数 + 0 = 0.6931471
doc 1 分数 = 0.6931471 + 0 = 0.6931471
- 第二个 match 中
brown分数
doc 1 分数 = 0.21110919
doc 2 分数 = 0.160443
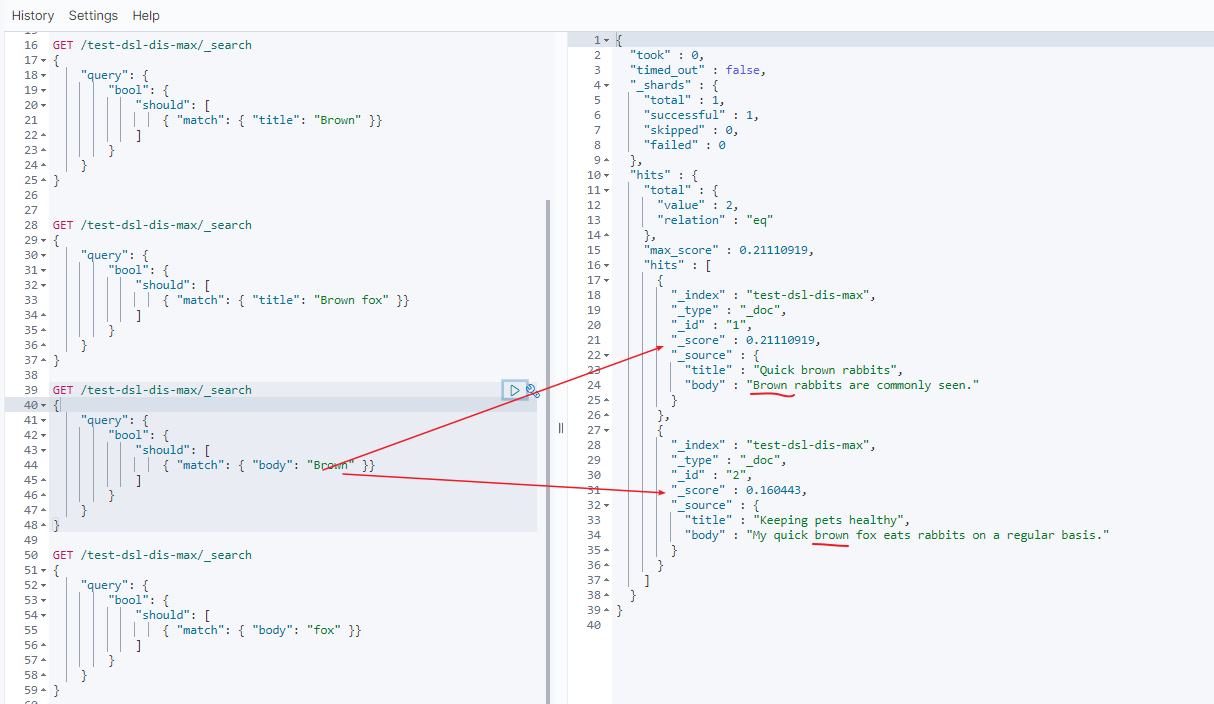
- 第二个 match 中
fox分数
doc 1 分数 = 0
doc 2 分数 = 0.60996956
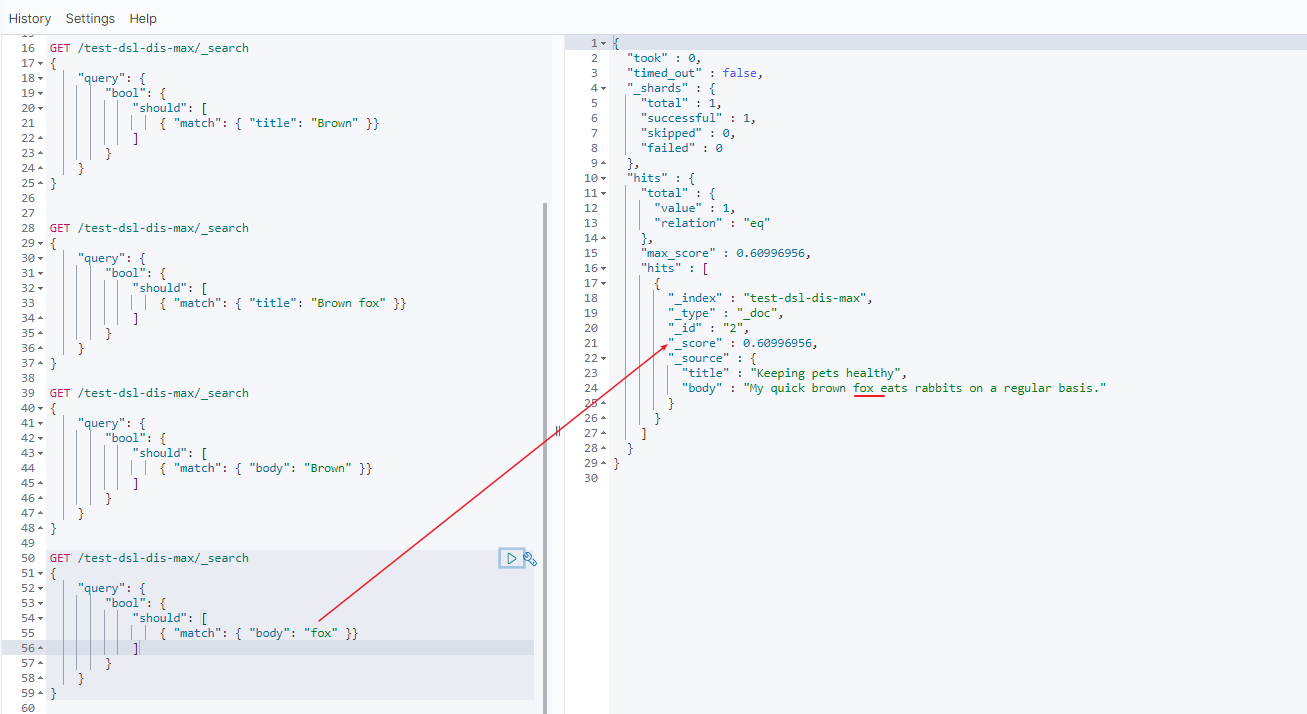
- 所以第二个 match 中
brown fox分数 = brown分数 + fox分数
doc 1 分数 = 0.21110919 + 0 = 0.21110919
doc 2 分数 = 0.160443 + 0.60996956 = 0.77041256
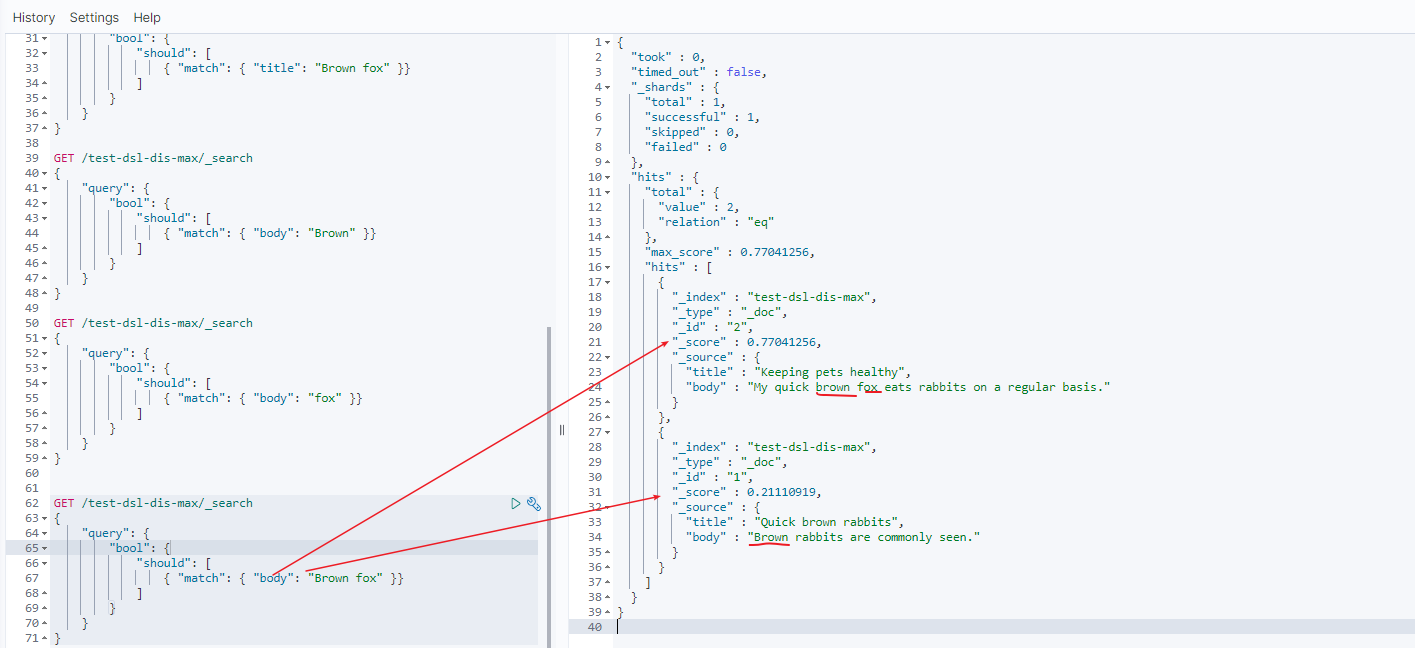
- 所以整个语句分数,
should分数 = 第一个match + 第二个match分数
doc 1 分数 = 0.6931471 + 0.21110919 = 0.90425634
doc 2 分数 = 0 + 0.77041256 = 0.77041256
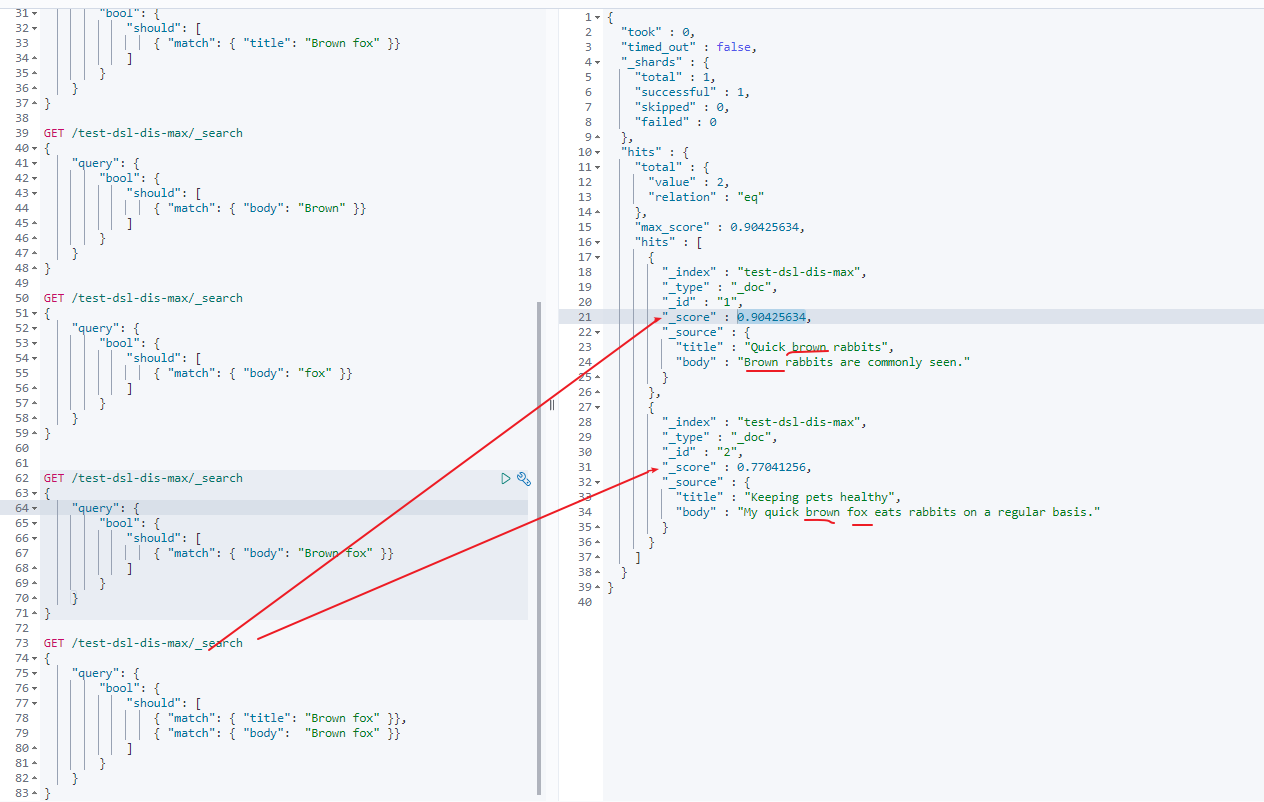
- 引入了dis_max
不使用 bool 查询,可以使用 dis_max 即分离 最大化查询(Disjunction Max Query) 。分离(Disjunction)的意思是 或(or) ,这与可以把结合(conjunction)理解成 与(and) 相对应。分离最大化查询(Disjunction Max Query)指的是: 将任何与任一查询匹配的文档作为结果返回,但只将最佳匹配的评分作为查询的评分结果返回 :
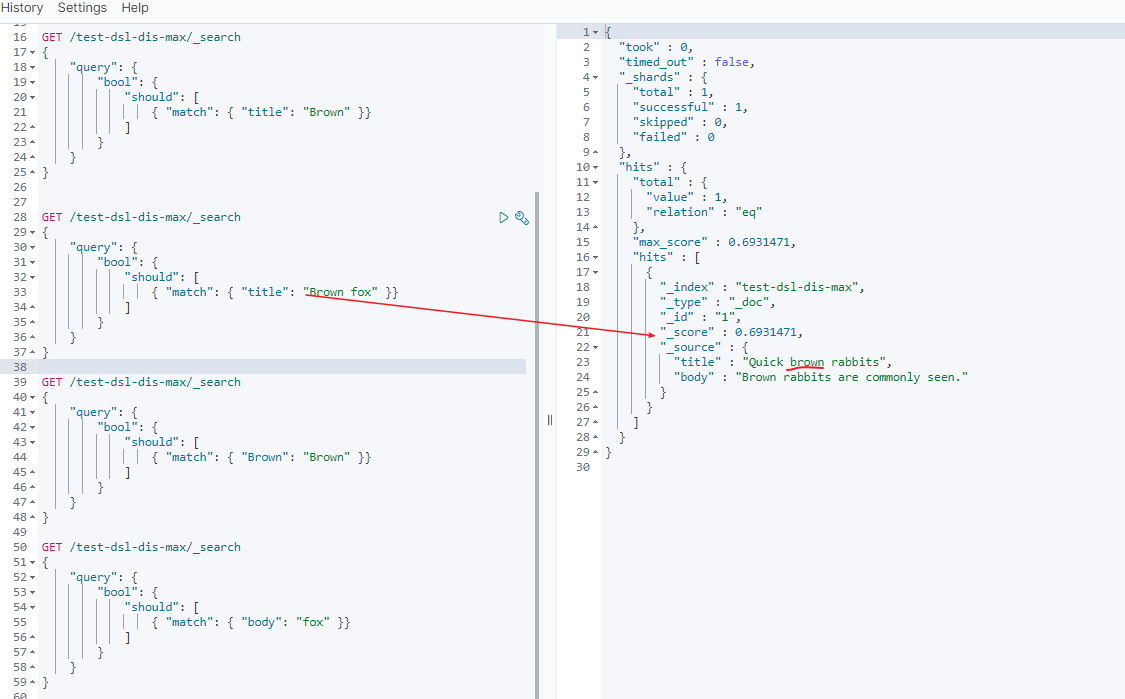
1 | GET /test-dsl-dis-max/_search |
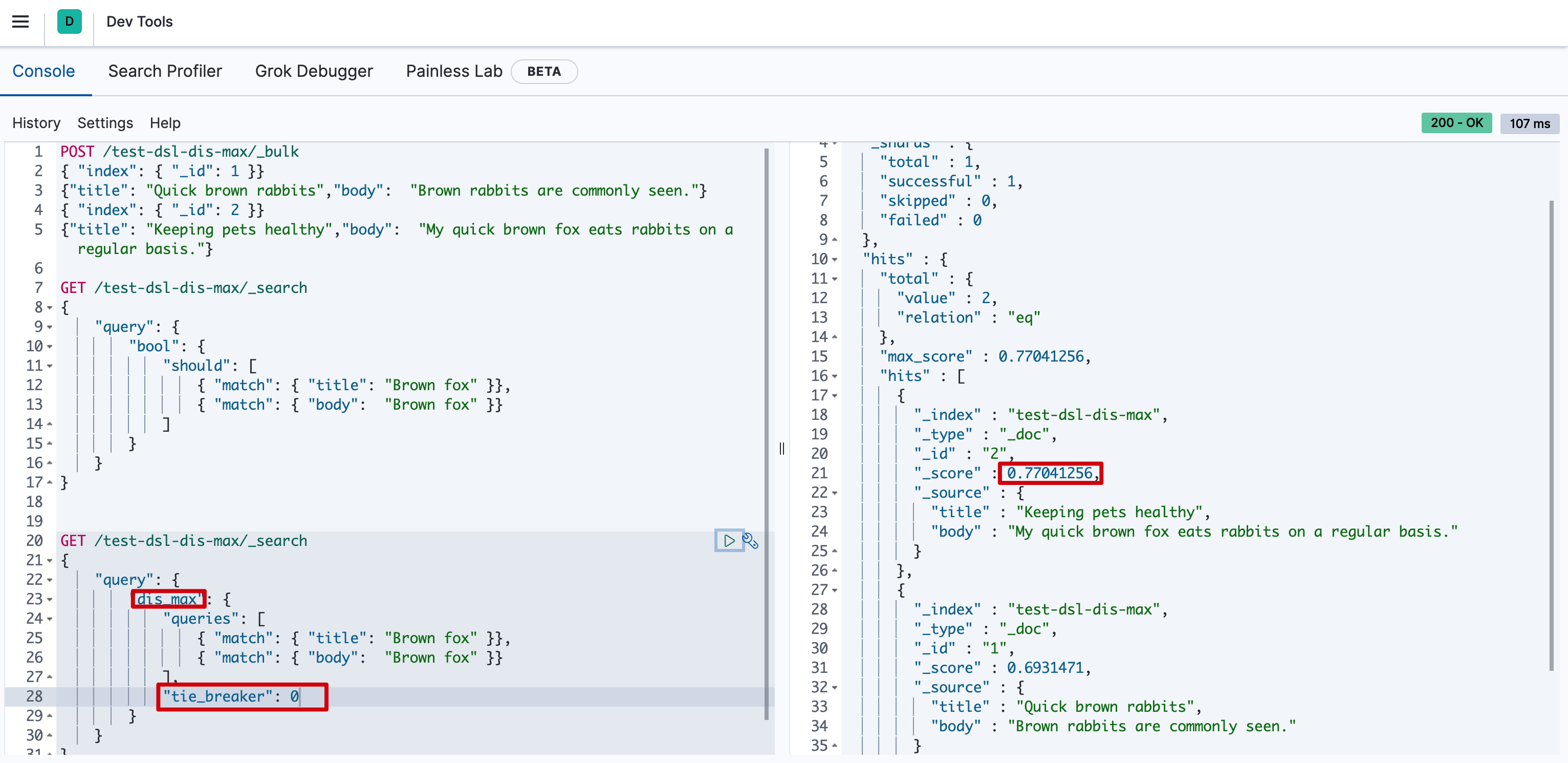
0.77041256怎么来的呢? 下文给你解释它如何计算出来的。
- dis_max 条件的计算分数
分数 = 第一个匹配条件分数 + tie_breaker * 第二个匹配的条件的分数 …
1 | GET /test-dsl-dis-max/_search |
doc 1 分数 = 0.6931471 + 0.21110919 * 0 = 0.6931471
doc 2 分数 = 0.77041256 = 0.77041256
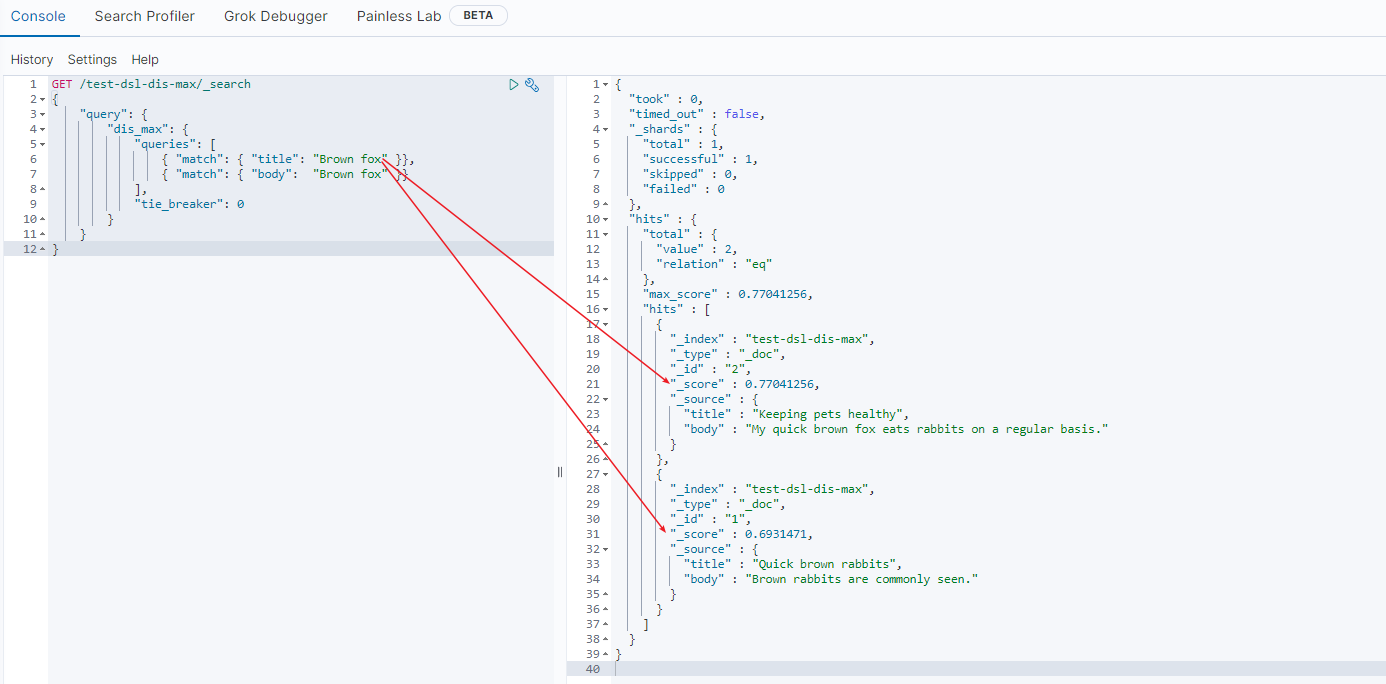
这样你就能理解通过dis_max将doc 2 置前了, 当然这里如果缺省tie_breaker字段的话默认就是0,你还可以设置它的比例(在0到1之间)来控制排名。(显然值为1时和should查询是一致的)
function_score(函数查询)
简而言之就是用自定义function的方式来计算_score。
可以ES有哪些自定义function呢?
script_score使用自定义的脚本来完全控制分值计算逻辑。如果你需要以上预定义函数之外的功能,可以根据需要通过脚本进行实现。weight对每份文档适用一个简单的提升,且该提升不会被归约:当weight为2时,结果为2 * _score。random_score使用一致性随机分值计算来对每个用户采用不同的结果排序方式,对相同用户仍然使用相同的排序方式。field_value_factor使用文档中某个字段的值来改变_score,比如将受欢迎程度或者投票数量考虑在内。衰减函数(Decay Function)-linear,exp,gauss
例子
以最简单的random_score 为例
1 | GET /_search |
进一步的,它还可以使用上述function的组合(functions)
1 | GET /_search |
script_score 可以使用如下方式
1 | GET /_search |
更多相关内容,可以参考官方文档 PS: 形成体系化认知以后,具体用的时候查询下即可。
参考文章
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/compound-queries.html
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/query-dsl-bool-query.html
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.12/query-dsl-function-score-query.html