38 集群容错:一个好汉三个帮(下)
你好,我是杨四正,今天我和你分享的主题是集群容错:一个好汉三个帮(下篇)。
在上一课时,我们介绍了 Dubbo Cluster 层中集群容错机制的基础知识,还说明了 Cluster 接口的定义以及其各个实现类的核心功能。同时,我们还分析了 AbstractClusterInvoker 抽象类以及 AbstractCluster 抽象实现类的核心实现。
那接下来在本课时,我们将介绍 Cluster 接口的全部实现类,以及相关的 Cluster Invoker 实现类。
FailoverClusterInvoker
通过前面对 Cluster 接口的介绍我们知道,Cluster 默认的扩展实现是 FailoverCluster,其 doJoin() 方法中会创建一个 FailoverClusterInvoker 对象并返回,具体实现如下:
1
2
3
| public <T> AbstractClusterInvoker<T> doJoin(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException {
return new FailoverClusterInvoker<>(directory);
}
|
FailoverClusterInvoker 会在调用失败的时候,自动切换 Invoker 进行重试。下面来看 FailoverClusterInvoker 的核心实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, final List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
List<Invoker<T>> copyInvokers = invokers;
// 检查copyInvokers集合是否为空,如果为空会抛出异常
checkInvokers(copyInvokers, invocation);
String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
// 参数重试次数,默认重试2次,总共执行3次
int len = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, RETRIES_KEY, DEFAULT_RETRIES) + 1;
if (len <= 0) {
len = 1;
}
RpcException le = null;
// 记录已经尝试调用过的Invoker对象
List<Invoker<T>> invoked = new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>(copyInvokers.size());
Set<String> providers = new HashSet<String>(len);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// 第一次传进来的invokers已经check过了,第二次则是重试,需要重新获取最新的服务列表
if (i > 0) {
checkWhetherDestroyed();
// 这里会重新调用Directory.list()方法,获取Invoker列表
copyInvokers = list(invocation);
// 检查copyInvokers集合是否为空,如果为空会抛出异常
checkInvokers(copyInvokers, invocation);
}
// 通过LoadBalance选择Invoker对象,这里传入的invoked集合,
// 就是前面介绍AbstractClusterInvoker.select()方法中的selected集合
Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, copyInvokers, invoked);
// 记录此次要尝试调用的Invoker对象,下一次重试时就会过滤这个服务
invoked.add(invoker);
RpcContext.getContext().setInvokers((List) invoked);
try {
// 调用目标Invoker对象的invoke()方法,完成远程调用
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
// 经过尝试之后,终于成功,这里会打印一个警告日志,将尝试过来的Provider地址打印出来
if (le != null && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("...");
}
return result;
} catch (RpcException e) {
if (e.isBiz()) { // biz exception.
throw e;
}
le = e;
} catch (Throwable e) { // 抛出异常,表示此次尝试失败,会进行重试
le = new RpcException(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
// 记录尝试过的Provider地址,会在上面的警告日志中打印出来
providers.add(invoker.getUrl().getAddress());
}
}
// 达到重试次数上限之后,会抛出异常,其中会携带调用的方法名、尝试过的Provider节点的地址(providers集合)、全部的Provider个数(copyInvokers集合)以及Directory信息
throw new RpcException(le.getCode(), "...");
}
|
FailbackClusterInvoker
FailbackCluster 是 Cluster 接口的另一个扩展实现,扩展名是 failback,其 doJoin() 方法中创建的 Invoker 对象是 FailbackClusterInvoker 类型,具体实现如下:
1
2
3
| public <T> AbstractClusterInvoker<T> doJoin(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException {
return new FailbackClusterInvoker<>(directory);
}
|
FailbackClusterInvoker 在请求失败之后,返回一个空结果给 Consumer,同时还会添加一个定时任务对失败的请求进行重试。下面来看 FailbackClusterInvoker 的具体实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| protected Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
Invoker<T> invoker = null;
try {
// 检测Invoker集合是否为空
checkInvokers(invokers, invocation);
// 调用select()方法得到此次尝试的Invoker对象
invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, null);
// 调用invoke()方法完成远程调用
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
} catch (Throwable e) {
// 请求失败之后,会添加一个定时任务进行重试
addFailed(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, invoker);
return AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult(null, null, invocation); // 请求失败时,会返回一个空结果
}
}
|
在 doInvoke() 方法中,请求失败时会调用 addFailed() 方法添加定时任务进行重试,默认每隔 5 秒执行一次,总共重试 3 次,具体实现如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| private void addFailed(LoadBalance loadbalance, Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, Invoker<T> lastInvoker) {
if (failTimer == null) {
synchronized (this) {
if (failTimer == null) { // Double Check防止并发问题
// 初始化时间轮,这个时间轮有32个槽,每个槽代表1秒
failTimer = new HashedWheelTimer(
new NamedThreadFactory("failback-cluster-timer", true),
1,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, 32, failbackTasks);
}
}
}
// 创建一个定时任务
RetryTimerTask retryTimerTask = new RetryTimerTask(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, lastInvoker, retries, RETRY_FAILED_PERIOD);
try {
// 将定时任务添加到时间轮中
failTimer.newTimeout(retryTimerTask, RETRY_FAILED_PERIOD, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error("...");
}
}
|
在 RetryTimerTask 定时任务中,会重新调用 select() 方法筛选合适的 Invoker 对象,并尝试进行请求。如果请求再次失败且重试次数未达到上限,则调用 rePut() 方法再次添加定时任务,等待进行重试;如果请求成功,也不会返回任何结果。RetryTimerTask 的核心实现如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| public void run(Timeout timeout) {
try {
// 重新选择Invoker对象,注意,这里会将上次重试失败的Invoker作为selected集合传入
Invoker<T> retryInvoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, Collections.singletonList(lastInvoker));
lastInvoker = retryInvoker;
retryInvoker.invoke(invocation); // 请求对应的Provider节点
} catch (Throwable e) {
if ((++retryTimes) >= retries) { // 重试次数达到上限,输出警告日志
logger.error("...");
} else {
rePut(timeout); // 重试次数未达到上限,则重新添加定时任务,等待重试
}
}
}
private void rePut(Timeout timeout) {
if (timeout == null) { // 边界检查
return;
}
Timer timer = timeout.timer();
if (timer.isStop() || timeout.isCancelled()) { // 检查时间轮状态、检查定时任务状态
return;
}
// 重新添加定时任务
timer.newTimeout(timeout.task(), tick, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
|
FailfastClusterInvoker
FailfastCluster 的扩展名是 failfast,在其 doJoin() 方法中会创建 FailfastClusterInvoker 对象,具体实现如下:
1
2
3
| public <T> AbstractClusterInvoker<T> doJoin(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException {
return new FailfastClusterInvoker<>(directory);
}
|
FailfastClusterInvoker 只会进行一次请求,请求失败之后会立即抛出异常,这种策略适合非幂等的操作,具体实现如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
checkInvokers(invokers, invocation);
// 调用select()得到此次要调用的Invoker对象
Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, null);
try {
return invoker.invoke(invocation); // 发起请求
} catch (Throwable e) {
// 请求失败,直接抛出异常
if (e instanceof RpcException && ((RpcException) e).isBiz()) {
throw (RpcException) e;
}
throw new RpcException("...");
}
}
|
FailsafeClusterInvoker
FailsafeCluster 的扩展名是 failsafe,在其 doJoin() 方法中会创建 FailsafeClusterInvoker 对象,具体实现如下:
1
2
3
| public <T> AbstractClusterInvoker<T> doJoin(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException {
return new FailsafeClusterInvoker<>(directory);
}
|
FailsafeClusterInvoker 只会进行一次请求,请求失败之后会返回一个空结果,具体实现如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
try {
// 检测Invoker集合是否为空
checkInvokers(invokers, invocation);
// 调用select()得到此次要调用的Invoker对象
Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, null);
// 发起请求
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
} catch (Throwable e) {
// 请求失败之后,会打印一行日志并返回空结果
logger.error("...");
return AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult(null, null, invocation);
}
}
|
ForkingClusterInvoker
ForkingCluster 的扩展名称为 forking,在其 doJoin() 方法中,会创建一个 ForkingClusterInvoker 对象,具体实现如下:
1
2
3
| public <T> AbstractClusterInvoker<T> doJoin(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException {
return new ForkingClusterInvoker<>(directory);
}
|
ForkingClusterInvoker 中会维护一个线程池(executor 字段,通过 Executors.newCachedThreadPool() 方法创建的线程池),并发调用多个 Provider 节点,只要有一个 Provider 节点成功返回了结果,ForkingClusterInvoker 的 doInvoke() 方法就会立即结束运行。
ForkingClusterInvoker 主要是为了应对一些实时性要求较高的读操作,因为没有并发控制的多线程写入,可能会导致数据不一致。
ForkingClusterInvoker.doInvoke() 方法首先从 Invoker 集合中选出指定个数(forks 参数决定)的 Invoker 对象,然后通过 executor 线程池并发调用这些 Invoker,并将请求结果存储在 ref 阻塞队列中,则当前线程会阻塞在 ref 队列上,等待第一个请求结果返回。下面是 ForkingClusterInvoker 的具体实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
| public Result doInvoke(final Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
try {
// 检查Invoker集合是否为空
checkInvokers(invokers, invocation);
final List<Invoker<T>> selected;
// 从URL中获取forks参数,作为并发请求的上限,默认值为2
final int forks = getUrl().getParameter(FORKS_KEY, DEFAULT_FORKS);
final int timeout = getUrl().getParameter(TIMEOUT_KEY, DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
if (forks <= 0 || forks >= invokers.size()) {
// 如果forks为负数或是大于Invoker集合的长度,会直接并发调用全部Invoker
selected = invokers;
} else {
// 按照forks指定的并发度,选择此次并发调用的Invoker对象
selected = new ArrayList<>(forks);
while (selected.size() < forks) {
Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, selected);
if (!selected.contains(invoker)) {
selected.add(invoker); // 避免重复选择
}
}
}
RpcContext.getContext().setInvokers((List) selected);
// 记录失败的请求个数
final AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger();
// 用于记录请求结果
final BlockingQueue<Object> ref = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
for (final Invoker<T> invoker : selected) { // 遍历 selected 列表
executor.execute(() -> { // 为每个Invoker创建一个任务,并提交到线程池中
try {
// 发起请求
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
// 将请求结果写到ref队列中
ref.offer(result);
} catch (Throwable e) {
int value = count.incrementAndGet();
if (value >= selected.size()) {
// 如果失败的请求个数超过了并发请求的个数,则向ref队列中写入异常
ref.offer(e);
}
}
});
}
try {
// 当前线程会阻塞等待任意一个请求结果的出现
Object ret = ref.poll(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (ret instanceof Throwable) { // 如果结果类型为Throwable,则抛出异常
Throwable e = (Throwable) ret;
throw new RpcException("...");
}
return (Result) ret; // 返回结果
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RpcException("...");
}
} finally {
// 清除上下文信息
RpcContext.getContext().clearAttachments();
}
}
|
BroadcastClusterInvoker
BroadcastCluster 这个 Cluster 实现类的扩展名为 broadcast,在其 doJoin() 方法中创建的是 BroadcastClusterInvoker 类型的 Invoker 对象,具体实现如下:
1
2
3
| public <T> AbstractClusterInvoker<T> doJoin(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException {
return new BroadcastClusterInvoker<>(directory);
}
|
在 BroadcastClusterInvoker 中,会逐个调用每个 Provider 节点,其中任意一个 Provider 节点报错,都会在全部调用结束之后抛出异常。BroadcastClusterInvoker通常用于通知类的操作,例如通知所有 Provider 节点更新本地缓存。
下面来看 BroadcastClusterInvoker 的具体实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| public Result doInvoke(final Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
// 检测Invoker集合是否为空
checkInvokers(invokers, invocation);
RpcContext.getContext().setInvokers((List) invokers);
RpcException exception = null; // 用于记录失败请求的相关异常信息
Result result = null;
// 遍历所有Invoker对象
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
try {
// 发起请求
result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
} catch (RpcException e) {
exception = e;
logger.warn(e.getMessage(), e);
} catch (Throwable e) {
exception = new RpcException(e.getMessage(), e);
logger.warn(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
if (exception != null) { // 出现任何异常,都会在这里抛出
throw exception;
}
return result;
}
|
AvailableClusterInvoker
AvailableCluster 这个 Cluster 实现类的扩展名为 available,在其 join() 方法中创建的是 AvailableClusterInvoker 类型的 Invoker 对象,具体实现如下:
1
2
3
| public <T> Invoker<T> join(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException {
return new AvailableClusterInvoker<>(directory);
}
|
在 AvailableClusterInvoker 的 doInvoke() 方法中,会遍历整个 Invoker 集合,逐个调用对应的 Provider 节点,当遇到第一个可用的 Provider 节点时,就尝试访问该 Provider 节点,成功则返回结果;如果访问失败,则抛出异常终止遍历。
下面是 AvailableClusterInvoker 的具体实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) { // 遍历整个Invoker集合
if (invoker.isAvailable()) { // 检测该Invoker是否可用
// 发起请求,调用失败时的异常会直接抛出
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
}
// 没有找到可用的Invoker,也会抛出异常
throw new RpcException("No provider available in " + invokers);
}
|
MergeableClusterInvoker
MergeableCluster 这个 Cluster 实现类的扩展名为 mergeable,在其 doJoin() 方法中创建的是 MergeableClusterInvoker 类型的 Invoker 对象,具体实现如下:
1
2
3
| public <T> AbstractClusterInvoker<T> doJoin(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException {
return new MergeableClusterInvoker<T>(directory);
}
|
MergeableClusterInvoker 会对多个 Provider 节点返回结果合并。如果请求的方法没有配置 Merger 合并器(即没有指定 merger 参数),则不会进行结果合并,而是直接将第一个可用的 Invoker 结果返回。下面来看 MergeableClusterInvoker 的具体实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
| protected Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
checkInvokers(invokers, invocation);
String merger = getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), MERGER_KEY);
// 判断要调用的目标方法是否有合并器,如果没有,则不会进行合并,
// 找到第一个可用的Invoker直接调用并返回结果
if (ConfigUtils.isEmpty(merger)) {
for (final Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
if (invoker.isAvailable()) {
try {
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
} catch (RpcException e) {
if (e.isNoInvokerAvailableAfterFilter()) {
log.debug("No available provider for service" + getUrl().getServiceKey() + " on group " + invoker.getUrl().getParameter(GROUP_KEY) + ", will continue to try another group.");
} else {
throw e;
}
}
}
}
return invokers.iterator().next().invoke(invocation);
}
// 确定目标方法的返回值类型
Class<?> returnType;
try {
returnType = getInterface().getMethod(
invocation.getMethodName(), invocation.getParameterTypes()).getReturnType();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
returnType = null;
}
// 调用每个Invoker对象(异步方式),将请求结果记录到results集合中
Map<String, Result> results = new HashMap<>();
for (final Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
RpcInvocation subInvocation = new RpcInvocation(invocation, invoker);
subInvocation.setAttachment(ASYNC_KEY, "true");
results.put(invoker.getUrl().getServiceKey(), invoker.invoke(subInvocation));
}
Object result = null;
List<Result> resultList = new ArrayList<Result>(results.size());
// 等待结果返回
for (Map.Entry<String, Result> entry : results.entrySet()) {
Result asyncResult = entry.getValue();
try {
Result r = asyncResult.get();
if (r.hasException()) {
log.error("Invoke " + getGroupDescFromServiceKey(entry.getKey()) +
" failed: " + r.getException().getMessage(),
r.getException());
} else {
resultList.add(r);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RpcException("Failed to invoke service " + entry.getKey() + ": " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
if (resultList.isEmpty()) {
return AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult(invocation);
} else if (resultList.size() == 1) {
return resultList.iterator().next();
}
if (returnType == void.class) {
return AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult(invocation);
}
// merger如果以"."开头,后面为方法名,这个方法名是远程目标方法的返回类型中的方法
// 得到每个Provider节点返回的结果对象之后,会遍历每个返回对象,调用merger参数指定的方法
if (merger.startsWith(".")) {
merger = merger.substring(1);
Method method;
try {
method = returnType.getMethod(merger, returnType);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RpcException("Can not merge result because missing method [ " + merger + " ] in class [ " +
returnType.getName() + " ]");
}
if (!Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
method.setAccessible(true);
}
// resultList集合保存了所有的返回对象,method是Method对象,也就是merger指定的方法
// result是最后返回调用方的结果
result = resultList.remove(0).getValue();
try {
if (method.getReturnType() != void.class
&& method.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(result.getClass())) {
for (Result r : resultList) { // 反射调用
result = method.invoke(result, r.getValue());
}
} else {
for (Result r : resultList) { // 反射调用
method.invoke(result, r.getValue());
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RpcException("Can not merge result: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
} else {
Merger resultMerger;
if (ConfigUtils.isDefault(merger)) {
// merger参数为true或者default,表示使用默认的Merger扩展实现完成合并
// 在后面课时中会介绍Merger接口
resultMerger = MergerFactory.getMerger(returnType);
} else {
//merger参数指定了Merger的扩展名称,则使用SPI查找对应的Merger扩展实现对象
resultMerger = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Merger.class).getExtension(merger);
}
if (resultMerger != null) {
List<Object> rets = new ArrayList<Object>(resultList.size());
for (Result r : resultList) {
rets.add(r.getValue());
}
// 执行合并操作
result = resultMerger.merge(
rets.toArray((Object[]) Array.newInstance(returnType, 0)));
} else {
throw new RpcException("There is no merger to merge result.");
}
}
return AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult(result, invocation);
}
|
ZoneAwareClusterInvoker
ZoneAwareCluster 这个 Cluster 实现类的扩展名为 zone-aware,在其 doJoin() 方法中创建的是 ZoneAwareClusterInvoker 类型的 Invoker 对象,具体实现如下:
1
2
3
| protected <T> AbstractClusterInvoker<T> doJoin(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException {
return new ZoneAwareClusterInvoker<T>(directory);
}
|
在 Dubbo 中使用多个注册中心的架构如下图所示:
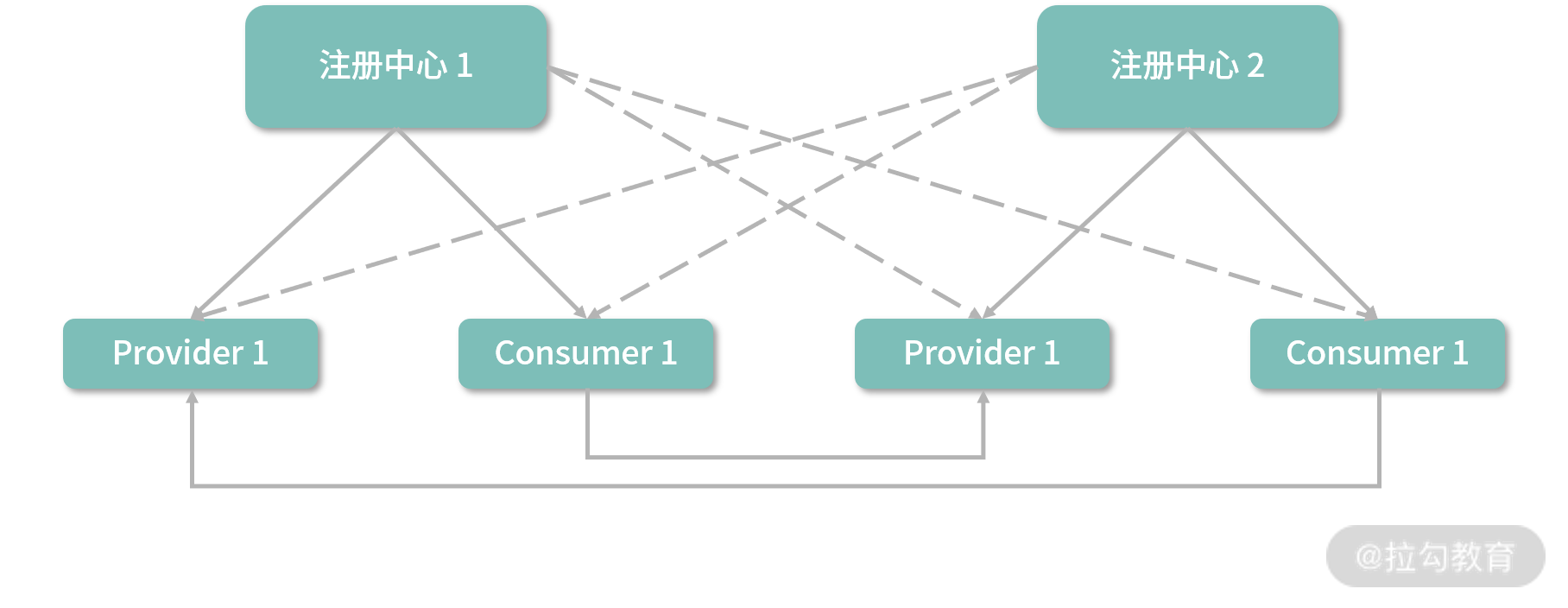
双注册中心结构图
Consumer 可以使用 ZoneAwareClusterInvoker 先在多个注册中心之间进行选择,选定注册中心之后,再选择 Provider 节点,如下图所示:
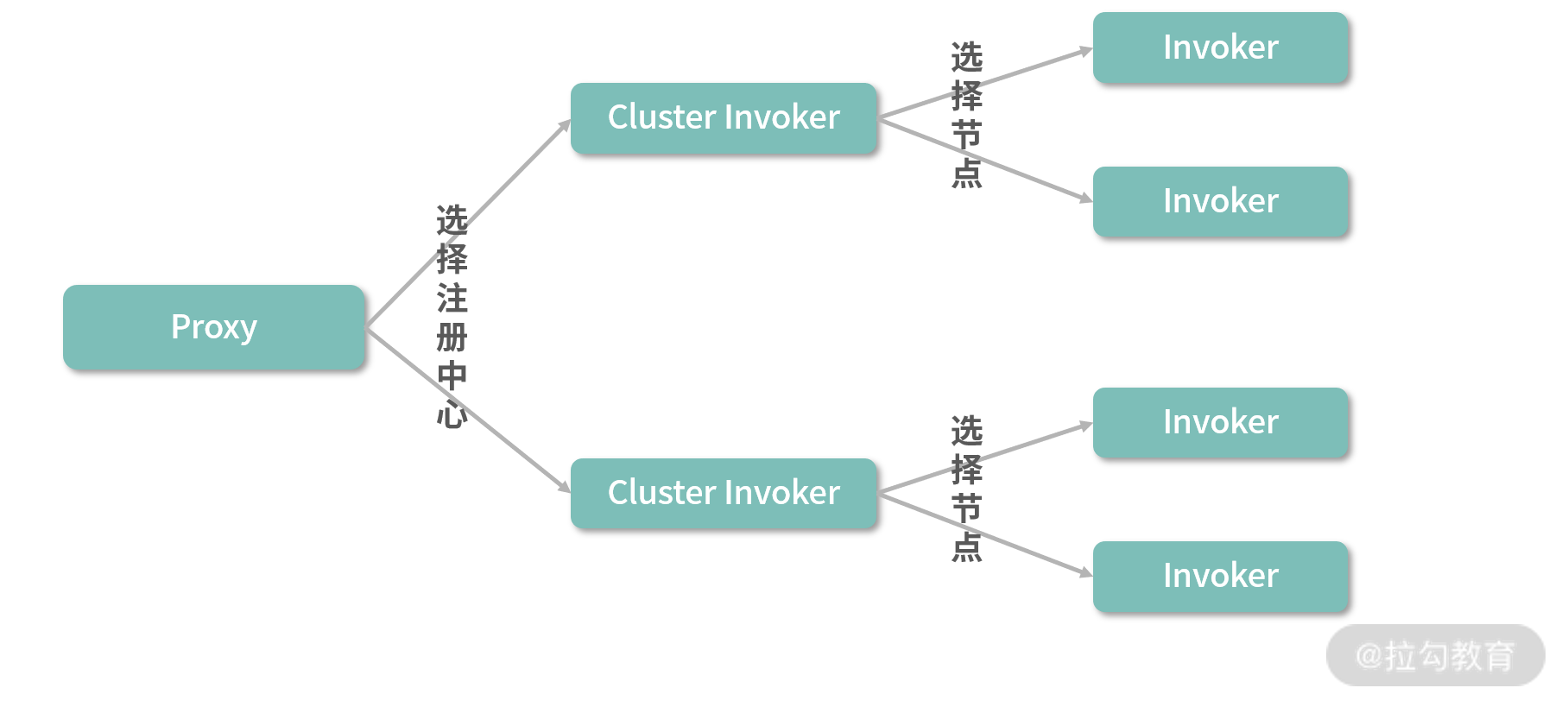
ZoneAwareClusterInvoker 在多注册中心之间进行选择的策略有以下四种。
- 找到preferred 属性为 true 的注册中心,它是优先级最高的注册中心,只有该中心无可用 Provider 节点时,才会回落到其他注册中心。
- 根据请求中的 zone key 做匹配,优先派发到相同 zone 的注册中心。
- 根据权重(也就是注册中心配置的 weight 属性)进行轮询。
- 如果上面的策略都未命中,则选择第一个可用的 Provider 节点。
下面来看 ZoneAwareClusterInvoker 的具体实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, final List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
// 首先找到preferred属性为true的注册中心,它是优先级最高的注册中心,只有该中心无可用 Provider 节点时,才会回落到其他注册中心
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
MockClusterInvoker<T> mockClusterInvoker = (MockClusterInvoker<T>) invoker;
if (mockClusterInvoker.isAvailable() && mockClusterInvoker.getRegistryUrl()
.getParameter(REGISTRY_KEY + "." + PREFERRED_KEY, false)) {
return mockClusterInvoker.invoke(invocation);
}
}
// 根据请求中的registry_zone做匹配,优先派发到相同zone的注册中心
String zone = (String) invocation.getAttachment(REGISTRY_ZONE);
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(zone)) {
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
MockClusterInvoker<T> mockClusterInvoker = (MockClusterInvoker<T>) invoker;
if (mockClusterInvoker.isAvailable() && zone.equals(mockClusterInvoker.getRegistryUrl().getParameter(REGISTRY_KEY + "." + ZONE_KEY))) {
return mockClusterInvoker.invoke(invocation);
}
}
String force = (String) invocation.getAttachment(REGISTRY_ZONE_FORCE);
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(force) && "true".equalsIgnoreCase(force)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("...");
}
}
// 根据权重(也就是注册中心配置的weight属性)进行轮询
Invoker<T> balancedInvoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, null);
if (balancedInvoker.isAvailable()) {
return balancedInvoker.invoke(invocation);
}
// 选择第一个可用的 Provider 节点
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
MockClusterInvoker<T> mockClusterInvoker = (MockClusterInvoker<T>) invoker;
if (mockClusterInvoker.isAvailable()) {
return mockClusterInvoker.invoke(invocation);
}
}
throw new RpcException("No provider available in " + invokers);
}
|
总结
本课时我们重点介绍了 Dubbo 中 Cluster 接口的各个实现类的原理以及相关 Invoker 的实现原理。这里重点分析的 Cluster 实现有:Failover Cluster、Failback Cluster、Failfast Cluster、Failsafe Cluster、Forking Cluster、Broadcast Cluster、Available Cluster 和 Mergeable Cluster。除此之外,我们还分析了多注册中心的 ZoneAware Cluster 实现。

