03 WebFlux Web CRUD 实践 上一篇基于功能性端点去创建一个简单服务,实现了 Hello。这一篇用 Spring Boot WebFlux 的注解控制层技术创建一个 CRUD WebFlux 应用,让开发更方便。这里我们不对数据库储存进行访问,因为后续会讲到,而且这里主要是讲一个完整的 WebFlux CRUD。
结构 这个工程会对城市(City)进行管理实现 CRUD 操作。该工程创建编写后,得到下面的结构,其目录结构如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 ├── pom.xml ├── src │ └── main │ ├── java │ │ └── org │ │ └── spring │ │ └── springboot │ │ ├── Application.java │ │ ├── dao │ │ │ └── CityRepository.java │ │ ├── domain │ │ │ └── City.java │ │ ├── handler │ │ │ └── CityHandler.java │ │ └── webflux │ │ └── controller │ │ └── CityWebFluxController.java │ └── resources │ └── application.properties └── target
如目录结构,我们需要编写的内容按顺序有:
对象 数据访问层类 Repository 处理器类 Handler 控制器类 Controller 对象 新建包 org.spring.springboot.domain,作为编写城市实体对象类。新建城市(City)对象 City,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 /** * 城市实体类 * */ public class City { /** * 城市编号 */ private Long id; /** * 省份编号 */ private Long provinceId; /** * 城市名称 */ private String cityName; /** * 描述 */ private String description; public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public Long getProvinceId() { return provinceId; } public void setProvinceId(Long provinceId) { this.provinceId = provinceId; } public String getCityName() { return cityName; } public void setCityName(String cityName) { this.cityName = cityName; } public String getDescription() { return description; } public void setDescription(String description) { this.description = description; } }
城市包含了城市编号、省份编号、城市名称和描述。具体开发中,会使用 Lombok 工具来消除冗长的 Java 代码,尤其是 POJO 的 getter / setter 方法,具体查看 Lombok 官网地址 。
数据访问层 CityRepository 新建包 org.spring.springboot.dao,作为编写城市数据访问层类 Repository。新建 CityRepository,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 import org.spring.springboot.domain.City; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong; @Repository public class CityRepository { private ConcurrentMap<Long, City> repository = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); private static final AtomicLong idGenerator = new AtomicLong(0); public Long save(City city) { Long id = idGenerator.incrementAndGet(); city.setId(id); repository.put(id, city); return id; } public Collection<City> findAll() { return repository.values(); } public City findCityById(Long id) { return repository.get(id); } public Long updateCity(City city) { repository.put(city.getId(), city); return city.getId(); } public Long deleteCity(Long id) { repository.remove(id); return id; } }
@Repository 用于标注数据访问组件,即 DAO 组件。实现代码中使用名为 repository 的 Map 对象作为内存数据存储,并对对象具体实现了具体业务逻辑。CityRepository 负责将 Book 持久层(数据操作)相关的封装组织,完成新增、查询、删除等操作。
这里不会涉及到数据存储这块,具体数据存储会在后续介绍。
处理器类 Handler 新建包 org.spring.springboot.handler,作为编写城市处理器类 CityHandler。新建 CityHandler,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 import org.spring.springboot.dao.CityRepository; import org.spring.springboot.domain.City; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import reactor.core.publisher.Flux; import reactor.core.publisher.Mono; @Component public class CityHandler { private final CityRepository cityRepository; @Autowired public CityHandler(CityRepository cityRepository) { this.cityRepository = cityRepository; } public Mono<Long> save(City city) { return Mono.create(cityMonoSink -> cityMonoSink.success(cityRepository.save(city))); } public Mono<City> findCityById(Long id) { return Mono.justOrEmpty(cityRepository.findCityById(id)); } public Flux<City> findAllCity() { return Flux.fromIterable(cityRepository.findAll()); } public Mono<Long> modifyCity(City city) { return Mono.create(cityMonoSink -> cityMonoSink.success(cityRepository.updateCity(city))); } public Mono<Long> deleteCity(Long id) { return Mono.create(cityMonoSink -> cityMonoSink.success(cityRepository.deleteCity(id))); } }
@Component 泛指组件,当组件不好归类的时候,使用该注解进行标注,然后用 final 和 @Autowired 标注在构造器注入 CityRepository Bean,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 private final CityRepository cityRepository; @Autowired public CityHandler(CityRepository cityRepository) { this.cityRepository = cityRepository; }
从返回值可以看出,Mono 和 Flux 适用于两个场景,即:
Mono:实现发布者,并返回 0 或 1 个元素,即单对象。 Flux:实现发布者,并返回 N 个元素,即 List 列表对象。 有人会问,这为啥不直接返回对象,比如返回 City/Long/List。原因是,直接使用 Flux 和 Mono 是非阻塞写法,相当于回调方式。利用函数式可以减少了回调,因此会看不到相关接口。这恰恰是 WebFlux 的好处:集合了非阻塞 + 异步。
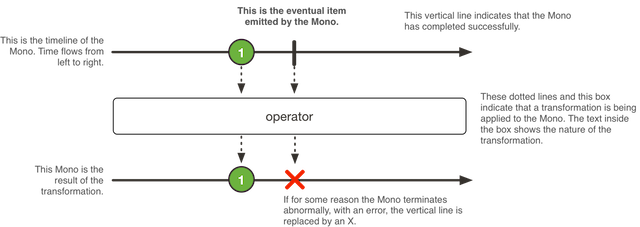
Mono Mono 是什么? 官方描述如下:A Reactive Streams Publisher with basic rx operators that completes successfully by emitting an element, or with an error.
Mono 是响应流 Publisher 具有基础 rx 操作符,可以成功发布元素或者错误,如图所示:
Mono 常用的方法有:
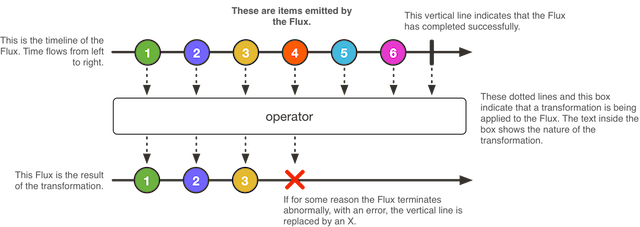
Mono.create():使用 MonoSink 来创建 Mono。 Mono.justOrEmpty():从一个 Optional 对象或 null 对象中创建 Mono。 Mono.error():创建一个只包含错误消息的 Mono。 Mono.never():创建一个不包含任何消息通知的 Mono。 Mono.delay():在指定的延迟时间之后,创建一个 Mono,产生数字 0 作为唯一值。 Flux Flux 是什么?官方描述如下:A Reactive Streams Publisher with rx operators that emits 0 to N elements, and then completes (successfully or with an error).
Flux 是响应流 Publisher 具有基础 rx 操作符,可以成功发布 0 到 N 个元素或者错误。Flux 其实是 Mono 的一个补充,如图所示:
所以要注意:如果知道 Publisher 是 0 或 1 个,则用 Mono。
Flux 最值得一提的是 fromIterable 方法,fromIterable(Iterable it) 可以发布 Iterable 类型的元素。当然,Flux 也包含了基础的操作:map、merge、concat、flatMap、take,这里就不展开介绍了。
控制器类 Controller Spring Boot WebFlux 开发中,不需要配置。Spring Boot WebFlux 可以使用自动配置加注解驱动的模式来进行开发。
新建包目录 org.spring.springboot.webflux.controller,并在目录中创建名为 CityWebFluxController 来处理不同的 HTTP Restful 业务请求。代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 import org.spring.springboot.domain.City; import org.spring.springboot.handler.CityHandler; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; import reactor.core.publisher.Flux; import reactor.core.publisher.Mono; @RestController @RequestMapping(value = "/city") public class CityWebFluxController { @Autowired private CityHandler cityHandler; @GetMapping(value = "/{id}") public Mono<City> findCityById(@PathVariable("id") Long id) { return cityHandler.findCityById(id); } @GetMapping() public Flux<City> findAllCity() { return cityHandler.findAllCity(); } @PostMapping() public Mono<Long> saveCity(@RequestBody City city) { return cityHandler.save(city); } @PutMapping() public Mono<Long> modifyCity(@RequestBody City city) { return cityHandler.modifyCity(city); } @DeleteMapping(value = "/{id}") public Mono<Long> deleteCity(@PathVariable("id") Long id) { return cityHandler.deleteCity(id); } }
这里按照 REST 风格实现接口,那具体什么是 REST?
REST 是属于 Web 自身的一种架构风格,是在 HTTP 1.1 规范下实现的。Representational State Transfer 全称翻译为表现层状态转化。Resource:资源。比如 newsfeed;Representational:表现形式,比如用 JSON、富文本等;State Transfer:状态变化。通过 HTTP 动作实现。
理解 REST,要明白五个关键要素:
资源(Resource) 资源的表述(Representation) 状态转移(State Transfer) 统一接口(Uniform Interface) 超文本驱动(Hypertext Driven) 6 个主要特性:
面向资源(Resource Oriented) 可寻址(Addressability) 连通性(Connectedness) 无状态(Statelessness) 统一接口(Uniform Interface) 超文本驱动(Hypertext Driven) 具体这里就不一一展开,详见这里 。
请求入参、Filters、重定向、Conversion、formatting 等知识会和以前 MVC 的知识一样,详情见文档 。
运行工程 一个 CRUD 的 Spring Boot Webflux 工程就开发完毕了,下面运行工程验证下。使用 IDEA 右侧工具栏,点击 Maven Project Tab,点击使用下 Maven 插件的 install 命令,或者使用命令行的形式,在工程根目录下,执行 Maven 清理和安装工程的指令:
1 2 3 4 5 cd springboot-webflux-2-restful mvn clean install
在控制台中看到成功的输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 ... 省略 [INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------ [INFO] BUILD SUCCESS [INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------ [INFO] Total time: 01:30 min [INFO] Finished at: 2017-10-15T10:00:54+08:00 [INFO] Final Memory: 31M/174M [INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
在 IDEA 中执行 Application 类启动,任意正常模式或者 Debug 模式。可以在控制台看到成功运行的输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ... 省略 2018-04-10 08:43:39.932 INFO 2052 --- [ctor-http-nio-1] r.ipc.netty.tcp.BlockingNettyContext : Started HttpServer on /0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0:8080 2018-04-10 08:43:39.935 INFO 2052 --- [ main] o.s.b.web.embedded.netty.NettyWebServer : Netty started on port(s): 8080 2018-04-10 08:43:39.960 INFO 2052 --- [ main] org.spring.springboot.Application : Started Application in 6.547 seconds (JVM running for 9.851)
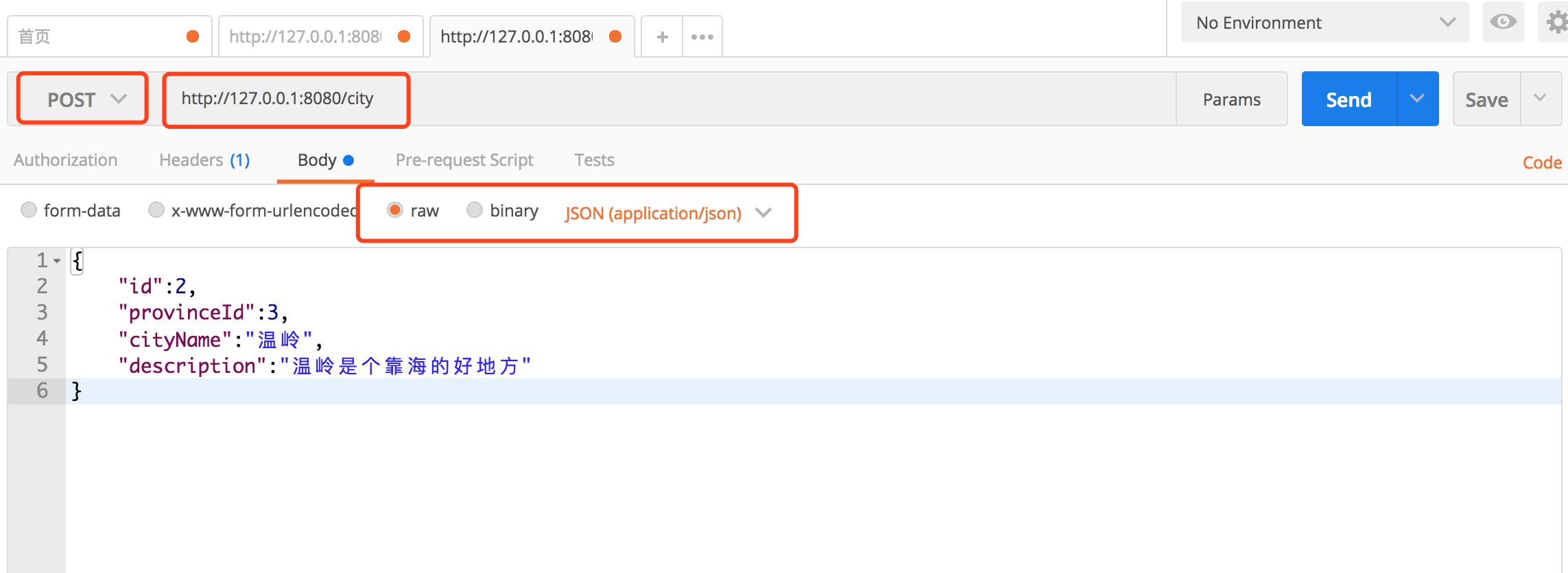
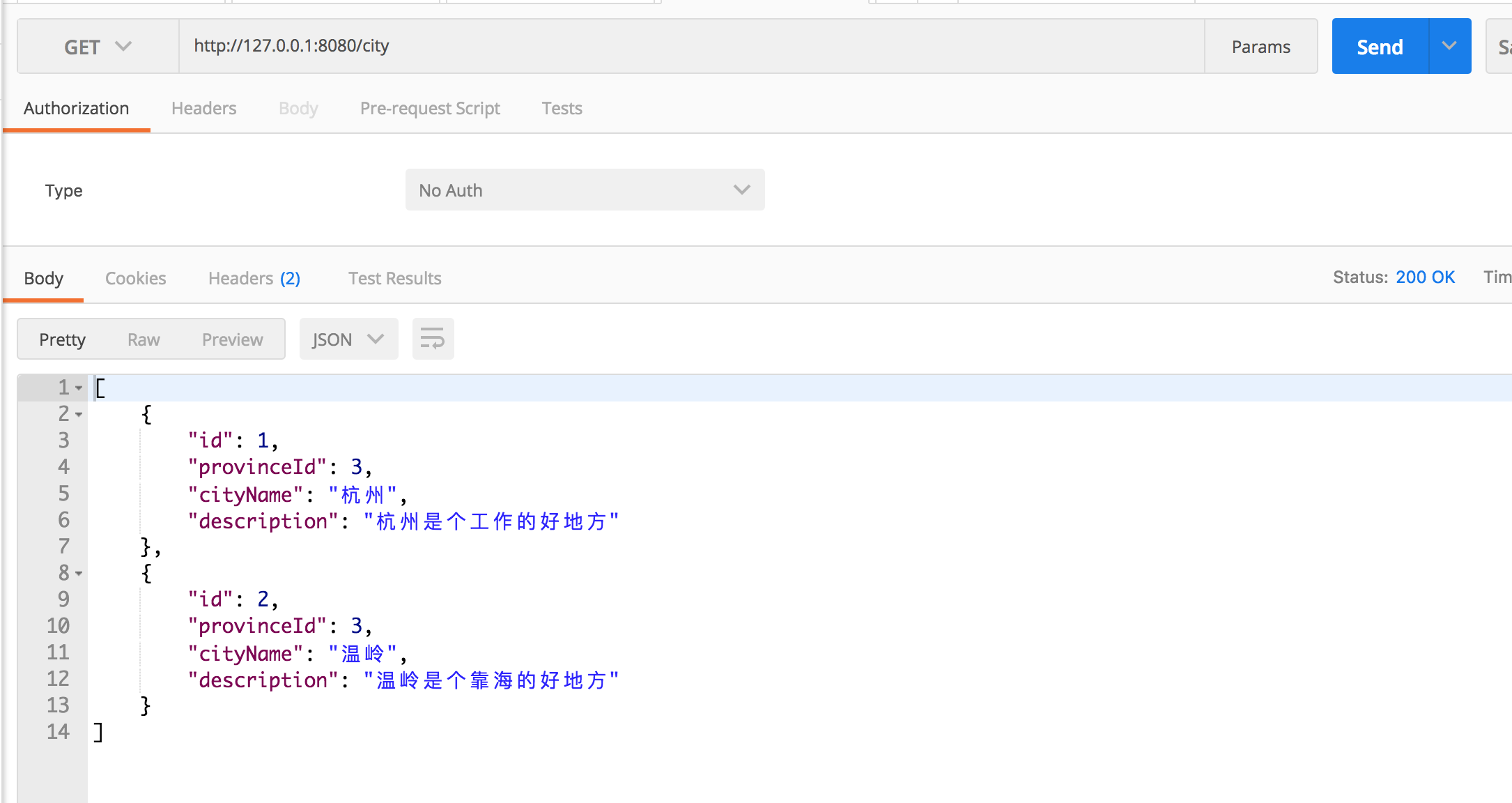
打开 POST MAN 工具,开发必备。进行下面操作:
新增城市信息 POST http://127.0.0.1:8080/city
获取城市信息列表 GET http://127.0.0.1:8080/city
其他接口就不演示了。
总结 这里,探讨了 Spring WebFlux 的一些功能,构建没有底层数据库的基本 CRUD 工程。为了更好的展示了如何创建 Flux 流,以及如何对其进行操作,下篇内容会讲到如何操作数据存储。